Transscandinavian Igneous Belt on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
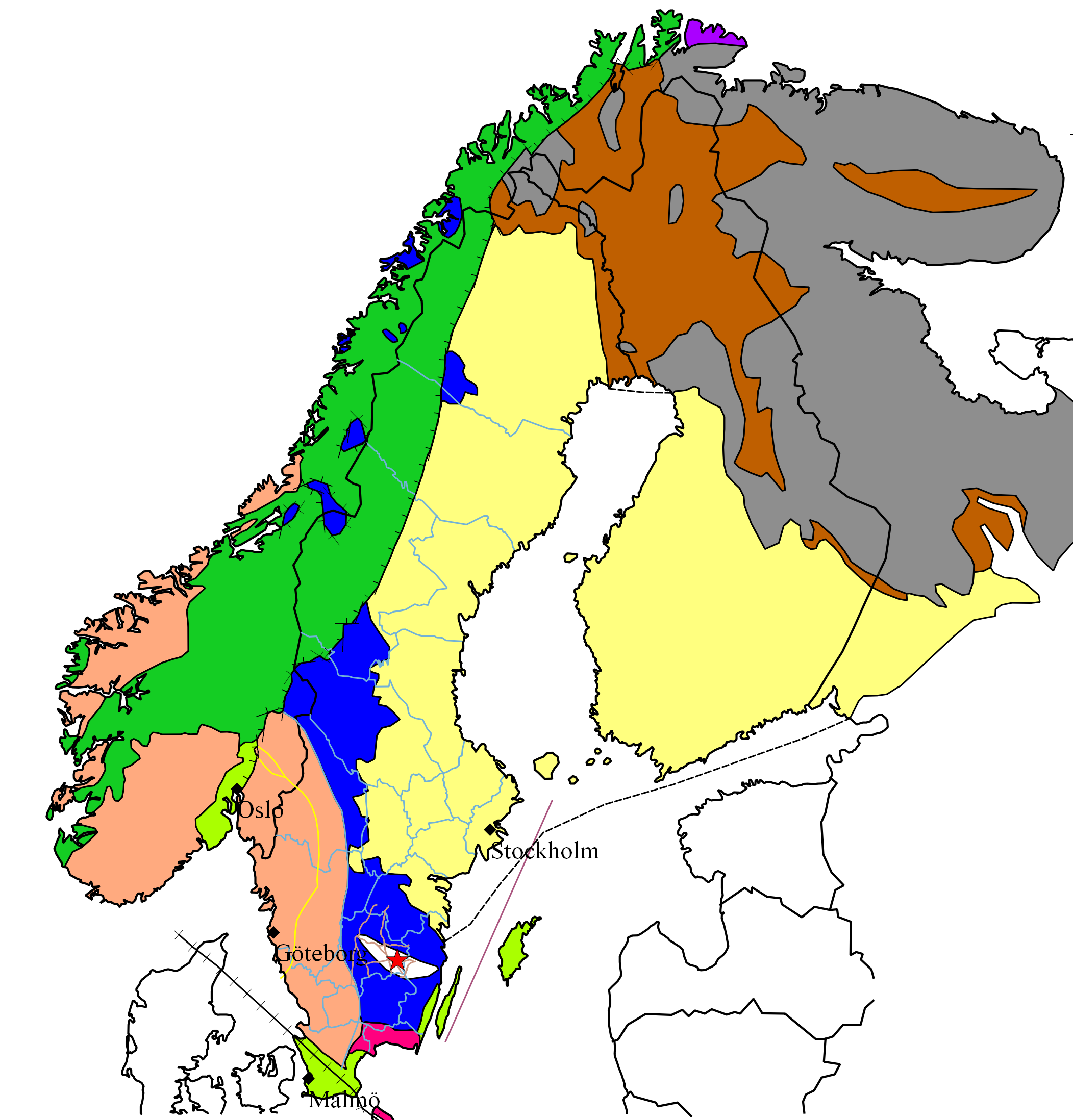 The Transscandinavian Igneous Belt ( sv, Transskandinaviska magmatiska bältet), abbreviated TIB, is one of the major
The Transscandinavian Igneous Belt ( sv, Transskandinaviska magmatiska bältet), abbreviated TIB, is one of the major
 The Transscandinavian Igneous Belt ( sv, Transskandinaviska magmatiska bältet), abbreviated TIB, is one of the major
The Transscandinavian Igneous Belt ( sv, Transskandinaviska magmatiska bältet), abbreviated TIB, is one of the major lithological
The lithology of a Rock (geology), rock unit is a description of its physical characteristics visible at outcrop, in hand or core sample, core samples, or with low magnification microscopy. Physical characteristics include colour, texture, grain ...
units of the Baltic Shield
The Baltic Shield (or Fennoscandian Shield) is a segment of the Earth's crust belonging to the East European Craton, representing a large part of Fennoscandia, northwestern Russia and the northern Baltic Sea. It is composed mostly of Archean and ...
. It consists of a series of batholith
A batholith () is a large mass of intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock), larger than in area, that forms from cooled magma deep in Earth's crust. Batholiths are almost always made mostly of felsic or intermediate rock types, such ...
s in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
and Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
forming a ca. 1400 km long belt running from Lofoten
Lofoten () is an archipelago and a traditional district in the county of Nordland, Norway. Lofoten has distinctive scenery with dramatic mountains and peaks, open sea and sheltered bays, beaches and untouched lands. There are two towns, Svolvær ...
, Norway, in the north to Blekinge
Blekinge (, old da, Bleking) is one of the traditional Swedish provinces (), situated in the southern coast of the geographic region of Götaland, in southern Sweden. It borders Småland, Scania and the Baltic Sea. It is the country's second ...
, Sweden, in the south. The Transscandinavian Igneous Belt and its rocks solidified from magma between 1810 and 1650 million years ago
The abbreviation Myr, "million years", is a unit of a quantity of (i.e. ) years, or 31.556926 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr (million years) is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya (million years ago). ...
during the Mesoproterozoic
The Mesoproterozoic Era is a geologic era that occurred from . The Mesoproterozoic was the first era of Earth's history for which a fairly definitive geological record survives. Continents existed during the preceding era (the Paleoproterozoic), ...
. The Transscandinavian Igneous Belt was likely formed in an Andean-type geological environment, implying it was once parallel to a destructive plate boundary.Lundqvist ''et al.'', p. 163–164 The belt was first identified in the 1980s and was referred as the "Transscandinavian Granite-Porphyry Belt". The current name was first applied in 1987.
Extent
The Transscandinavian Igneous Belt occurs as a ca. 1400 km long belt running fromLofoten
Lofoten () is an archipelago and a traditional district in the county of Nordland, Norway. Lofoten has distinctive scenery with dramatic mountains and peaks, open sea and sheltered bays, beaches and untouched lands. There are two towns, Svolvær ...
in the north to Blekinge
Blekinge (, old da, Bleking) is one of the traditional Swedish provinces (), situated in the southern coast of the geographic region of Götaland, in southern Sweden. It borders Småland, Scania and the Baltic Sea. It is the country's second ...
in the south.Lundqvist ''et al.'', p. 165–166 The northern parts of the belt are partly covered by Caledonian nappe
In geology, a nappe or thrust sheet is a large sheetlike body of rock (geology), rock that has been moved more than or above a thrust fault from its original position. Nappes form in compressional tectonic settings like continental collision z ...
s but crop out in windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for serv ...
(e.g. Rombak, Nasafjället). In addition to this some Caledonian nappes are made up of Transscandinavian Igneous Belt rocks. Beneath the East European Platform
East European Platform or Russian Platform is a large and flat area covered by sediments in Eastern Europe spanning from the Ural Mountains to the Tornquist Zone and from the Peri-Caspian Basin to the Barents Sea. Over geological time the platfor ...
the belt continues across the Baltic Sea to northeast Poland and Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast (russian: Калинингра́дская о́бласть, translit=Kaliningradskaya oblast') is the westernmost federal subject of Russia. It is a semi-exclave situated on the Baltic Sea. The largest city and administr ...
.
Chronology
Thepluton
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and com ...
s of the belt formed variously between 1810 and 1650 million years ago
The abbreviation Myr, "million years", is a unit of a quantity of (i.e. ) years, or 31.556926 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr (million years) is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya (million years ago). ...
(Mya) the oldest rocks overlapping in age with the rocks of the Svecofennian orogeny and the youngest overlapping in age with the deformation
Deformation can refer to:
* Deformation (engineering), changes in an object's shape or form due to the application of a force or forces.
** Deformation (physics), such changes considered and analyzed as displacements of continuum bodies.
* Defor ...
and metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chem ...
of the Gothian orogeny The Gothian orogeny ( sv, Gotiska orogenesen) or Kongsberg orogeny was an orogeny in western Fennoscandia that occurred between 1750 and 1500 million years ago. It precedes the younger Sveconorwegian orogeny that has overprinted much of it. The Go ...
. Three separate periods of igneous activity are recognised in the Transscandinavian Igneous Belt; TIB 1 (1813–1766 Mya), TIB 2 (1723–1691 Mya) and TIB 3 (1681–1657 Mya). This grouping is not perfect as it excludes the youngest units formed 1450 million years ago.
Hundreds of millions of years after the Transscandinavian Igneous Belt was formed it was subject to the particular deformation, tectonics and metamorphism of the Sveconorwegian orogeny
The Sveconorwegian orogeny was an orogenic system active 1140 to 960 million years ago and currently exposed as the Sveconorwegian orogenic belt in southwestern Sweden and southern Norway. In Norway the orogenic belt is exposed southeast of the f ...
about 1100 to 990 million years ago.
Lithology, petrology and geochemistry
Characteristically the granites and similar rocks of the Transscandinavian Igneous Belt are rich inalkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a ...
elements (e.g. sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable iso ...
and potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosphe ...
) and have porphyritic
Porphyritic is an adjective used in geology to describe igneous rocks with a distinct difference in the size of mineral crystals, with the larger crystals known as phenocrysts. Both extrusive and intrusive rocks can be porphyritic, meaning all ...
texture
Texture may refer to:
Science and technology
* Surface texture, the texture means smoothness, roughness, or bumpiness of the surface of an object
* Texture (roads), road surface characteristics with waves shorter than road roughness
* Texture (c ...
s. Not all rocks of the Transcandinavian Igneous Belt have a pure alkaline character, some display chemistries tending to the calc-alkaline magma series
The calc-alkaline magma series is one of two main subdivisions of the subalkaline magma series, the other subalkaline magma series being the tholeiitic series. A magma series is a series of compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic mag ...
. In addition to the above-mentioned rocks lesser amounts of mafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include ...
intrusives are also part of the belt.
References
Cited book * {{Geology of Fennoscandia Batholiths of Europe Geology of Norway Geology of Sweden Paleoproterozoic magmatism